
Starting from 2020.2, CLion also supports the Makefile build system.

STM32L5 and STM32U5 with TrustZone enabled.Just copy it into the generated project, look through all the “todo” comments, make the necessary changes, and then open it as a CLion project. The generated project is not supported, but there is an experimental snippet of CMakeLists.txt.
Unfortunately, there are some exceptions where this approach does not work: For most of the STM32 MCUs, the project sources may be generated with STM2CubeMX for STM32CubeIDE, and then opened with CLion directly. Q: Are all STM32 chips supported out of the box?Ī: The answer depends on the MCU series. At the moment our primary target is ARM Cortex-M kernels: on-chip debugging is fully supported there using SEGGER, ST-LINK, and some other debug adapters. For many other target platforms, like ARM or RISC-V, on-chip debugging is supported via the gdbserver protocol. For instance, AVR firmware can be compiled and flashed to the hardware, but an on-chip debugger is not supported because of hardware limitations. Q: Is it possible to debug on a microcontroller with CLion?Ī: That depends on the hardware type. CLion also offers special support for STM32 MCUs and a snippet of CMakeLists.txt, which may be a starting point for projects based on other MCU series. Please see our webhelp for the officially supported hardware types. For example, expressif32 ( ESP8266, ESP32 ), mips32 ( pic32 ), avr8 ( arduino ), and risc-v etc are likely to work fine. Q: What kind of bare-metal hardware is supported?Ī: While we don’t test CLion extensively with all possible types of hardware, in general, any hardware that is supported by a relatively recent GCC toolchain or by IAR compilers should work.

In some cases, on-chip debugging using SWD/JTAG can be helpful, and this is also supported via the Embedded GDB server. Here is an example project that demonstrates both embedded Linux support and a workaround for a related feature request. A project for Embedded Linux has to be compiled with a cross-compiler and then deployed and run on the target device under remote debugger. Skip analysis of file: C:/_disco D/JetBrains/CLionProjects/Untitled/main.For the specific instructions and details, check out our webhelp for Embedded Development in CLion. gcc-11.2.0/configure -host=x86_64-w64-mingw32 -target=x86_64-w64-mingw32 -build=x86_64-alpine-linux-musl -prefix=/win -enable-checking=release -enable-fully-dynamic-string -enable-languages=c,c++ -enable-libatomic -enable-libgomp -enable-libstdcxx-filesystem-ts=yes -enable-libstdcxx-time=yes -enable-seh-exceptions -enable-shared -enable-static -enable-threads=posix -enable-version-specific-runtime-libs -disable-bootstrap -disable-graphite -disable-libada -disable-libstdcxx-pch -disable-libstdcxx-debug -disable-libquadmath -disable-lto -disable-nls -disable-multilib -disable-rpath -disable-symvers -disable-werror -disable-win32-registry -with-gnu-as -with-gnu-ld -with-system-libiconv -with-system-libz -with-gmp=/win/makedepends -with-mpfr=/win/makedepends -with-mpc=/win/makedepends Probing compiler: ĬOLLECT_GCC=C:\_disco D\JetBrains\CLion\bin\mingw\bin\g++.exeĬonfigured with.
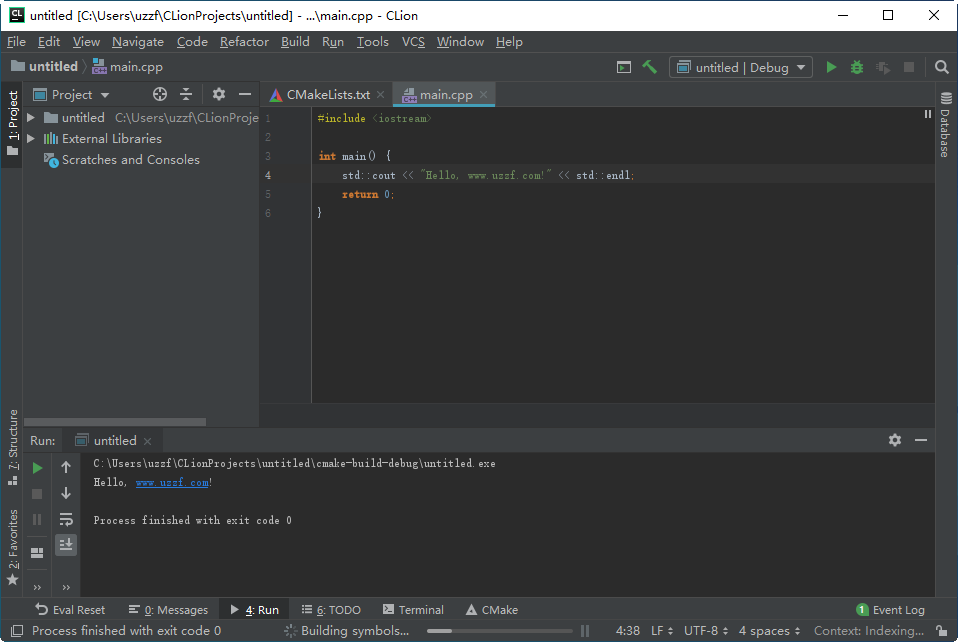
Language of file 'file:///C:/_disco%20D/JetBrains/CLionProjects/Untitled/main.cpp' is set to 'C++'Įxecute Sensor: Sonar Secrets Detection Sensor Std::cout << "String size is: " << s << std::endl Std::cout << "Hello, World!" << std::endl (Containing forced errors in source code) #include Request a Sonarlint analysis via contextual menu on main.cpp file.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
